Japan Market IT Services Outsourcing
April 17, 2023
With the speed of advances in digital transformation technologies, the need for faster response to customers’ IT service requests beside domestic constraints is becoming challenge.
In this series we will focus on offshoring and global outsourcing to find out few most often-asked questions like, how Japanese IT services market is? What the existing challenges at hand? How to deliver with quality to our customers? How India as offshoring and global outsourcing destination is? etc.
We have a global delivery centre in India, with global delivery experience of more than two decades. refer link:
https://www.intellilink.co.jp/en/global-delivery.aspx
Traditionally Japanese companies used to emphasis on in-house development. The major attention continues towards quality over quantity. But with the advances in software field, Japan could not adapt at pace like western countries adapted. Now with technological advances like Digital Transformations, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and cloud and demand from domestic and global customers, Japanese companies started facing lack of skilled human power. So, the companies started looking for opportunities to outsource IT services work.
To accomplish global delivery, one needs to identify challenges, risks, complexities, nuances. Need to adopt global mindset and bring agility to be successful in offshoring. With Global delivery mindset comes multiple opportunities as well as trade-offs. Top management commitment and directions are vital part for success of global delivery for any organization. The expectations from both parties Japanese prime company (who is outsourcing / offshoring) and the sub-contractor / offshore partner must be very transparent and clearly understood by both.
In this column let's understand overview of global and Japanese domestic IT services market followed by details specific to Japanese IT market.
1. IT services market overview
"IT services refer to the application of business and technical expertise to enable organizations in the creation, management, and optimization of or access to information and business processes." [8]
At high level segmentation of IT services market is as follows:
- ・IT consulting and implementation,
- ・IT Outsourcing,
- ・Business process Outsourcing,
- ・other IT services and support
The IT services industry serves multiple complementing multiple technologies to each other. Examples of IT service areas are application development and support (ADM), cloud services, Data and Intelligence, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), as well as cyber security services, salesforce etc.
Let's touch a bit on global and domestic IT service current market sizes and industry forecasts.
1.1. Global IT services size
Global IT services revenue is projected to achieve 1.2trnUSD by end of 2023. Expected to achieve 6.86% revenue annual growth rate CAGR 2023-27 with market volume projected at 1.57trnUSD by end of 2027. "IT Outsourcing" being the largest IT Service's segment with ~36% of market share, is projected to be 430.5bnUSD in 2023. [1]
Top 3 countries in IT services revenue generation are United States of America (USA), Japan and United Kingdom (UK). USA tops the most revenue generator with more than 40% of the total market share. Followed by Japan and UK with 8% of the total market size each.
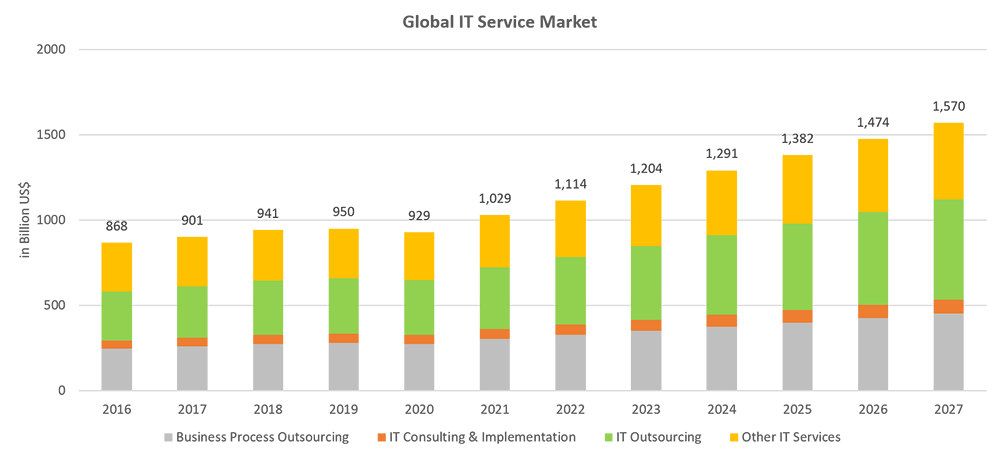
Figure 1: Global IT services market
Data Source: IT Services - Worldwide | Statista Market Forecast
1.2. Japan IT services size
The domestic IT service market was affected by the spread of the new coronavirus infection (COVID-19) in some areas, but the market as a whole has recovered steadily and turned to positive growth. Especially, demand for renovation/renewal of existing systems and DX-related demand drove the growth of the project-based market, resulting in a 3.2% year-on-year increase.
It will continue to grow steadily from 2022 onwards, expected to reach 91.31 bn USD in FY2023.IDC expects the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) to remain at 2.8% from 2021~2026, and is expected to reach 6,741 billion yen by end of 2026. [2]
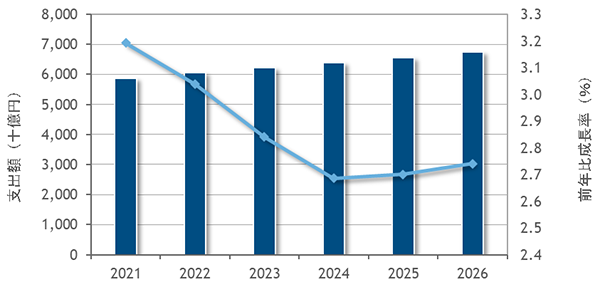
Figure 2: Japanese IT services market
Source: https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prJPJ48879822
| Company | Size(bn USD FY21) |
|---|---|
| Fujitsu | 8.6 |
| NTT DATA | 7.9 |
| Hitachi | 6.5 |
| NEC | 6.1 |
| IBM | 4.5 |
Table 1: Top players in Japan Market
Looking at Japanese IT services companies, NTT DATA in among the Top5 players along with Fujitsu, Hitachi, NEC, and IBM.
2. Japanese IT Services
Industries in Japan are becoming more efficient and adding more value with the accelerating digital transformation enabled by the development of ICT infrastructure and digital technology.
In this process integration of cyberspace and physical space is being facilitated. Looking at perspective movement from physical space to cyber space, government has started with multiple initiatives like "Society 5.0", "Beyond 5G promotion strategy" which drives the digital transformations. [6]
The workstyle innovations are prompted by the coronavirus pandemic is driving the growth in cloud market. The domestic cloud services market in 2019 was 2.3 trn JPY and expected to grow to 5.4 trn JPY by 2024. [6]
With tremendous progress of AI and IoT in recent years, the data generated is exponentially increasing. To process this data quantum computer and further innovations are in progress. The Japan domestic quantum computing market expected to reach 43 bn JPY by FY2025-26 and 230 bn JPY by FY2030-31. [6]
The digital transformations demand and lack of in-house skill, making it absolutely necessary to search for skilled pool of resources outside Japan.
As per our understanding organizations across globe offshore work from cost effectiveness. Based on our current experience, Japanese companies consider offshoring from many different customer centric objectives like:
- 1.Quality over quantity: no compromise on quality
- 2.Faster service to customers: speed to market, edge for competing in market.
- 3.Repeatable and predictable: no compromise on performance
- 4.Scalable and sustainable: long term relationship to cater future technological needs.
- 5.Cost effectiveness
Leaders from Japanese companies and their possible offshore partners need to have clarity on global delivery execution model. According to us, to decide model and bring more transparency, following factors awareness is fundamental key:
- -Market players
- -Formation: Existing Japanese structure for contracting partnerships
- -Resources: required skills and available human power,
- -Cultural barriers,
- -Organization maturity: Processes, tools etc
- -Security: IP, Data
- -Governance: Communication, KPIs, reviews,
- -Success Criteria for both
- -Other country specific environmental aspects and compliances.
Though every factor has its own importance, to start with in this column, lets primarily focus on Japanese market players, formation, resources. and offshoring overview.
2.1. Japan Market Map:
The market is divided in professional services, products services in B2B and B2C/C2C. There are some of the key players in IT services in Japan market. Widely we can group professional services and B2B competing players in three categories Domestic SI-ers, Foreign MNCs and Big4.
NTT DATA is focused on providing professional services in B2B space. Specializes in bringing together component subsystems as whole and ensures proper functioning.

Figure 3: Japan market map
Note: All logos are protected by respective laws. They are reproduced here for introductory and educational purposes only.
2.2. Formation
Sub-contracting in multiple layers is quite common in Japan and you may easily see 3rd or 4th Tier subcontracting happening. There are merits as well as demerits for this kind of formation. However, this is the way Japanese IT services industry functions. It’s a complete eco-system established and way of business working in Japan. The prime vendor and sub-contractors are selected based on trust and for long term collaboration, partnership.
Prime Vendor (SI-er: System Integrators) acts as the channel or an arm of Japanese corporates for their all-IT related needs. Existence of Prime Vendor is a crucial part of Japanese corporates. Prime Vendor provides all advice and services required by corporates like IT strategies, software adoptions etc.
Overall outsourcing / offshoring model work as follows: [7]
- 1.Project Basis order: when corporates require an IT service/solution, they initiate a customized order to their affiliated SI-er. This is treated as project.
- 2.Prime Vendors mostly have in-house capabilities to provide these IT services/solutions.
- 3.Based on the complexity and external speciality requirement, decision to outsource to sub-contractors will be decided.
- 4.Sub-Contractors based on their specific know-how in software development will take it further in-house/next level delegation.
- 5.Subject to the complexity of the work, there may even be subsequent delegation to downward sub-contractors as outsourcing.
- 6.This is the way the value chain is maintained, and kind of interdependency is established.
- 7.Coherency as main responsibility of the Prime Vendor. They are mainly responsible for all communication, collaboration, coordination to deliver integrated functionally working, secured service/solution to the corporate.
IT knowledge and talent are trapped within Prime Vendors, not with corporates. The same visualised in "Figure 5: ICT employees at Vendor companies vs User companies" as well.
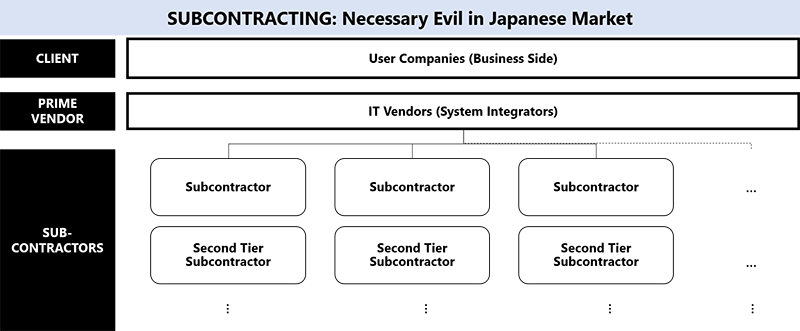
Figure 4: Forming Japan Corporate business Ecosystem
Merits:
- ・Low Cost: lesser fixed costs to Prime Vendors.
- ・Flexibility: to ramp-up/ramp-down resources.
- ・Multiple Options: flexibility to have multiple options/rates/capabilities.
- ・Strategic Alliances: possibility to create strategic alliances with different partners.
- ・Risk Sharing: efficient risk-sharing mechanism.
De-merits:
- ・Consumes a lot of coordination/management/integration efforts.
- ・Compliance / governance is a challenge for Prime.
- ・Prime vendor needs to comply with complicated sub-con laws.
- ・Sub-cons cannot grow much independently (leading to Kobanzame tendency)
In brief, the merits provide more flexibility in favour of corporates to get the best-in-class services, for Prime to deliver customer satisfaction and to sub-cons to get large floor to innovate, ideating and growing along with value chain. With current best practices in Japan, these de-merits can be addressed with proper planning and mitigations.
2.3. Resources
As an effect of contracting, sub-contracting, Japan stands out for having underpowered technology departments at user companies. In US and European countries almost 60~70% ICT professionals work for user companies. In contrast US and Europe, in Japan, 70+% of ICT professionals work for vendor companies.[4] This contradiction restricts corporates from in-house technology functions and makes firms more dependent on their technology providers. But this also adds value to corporates by concentrating mainly on core business.
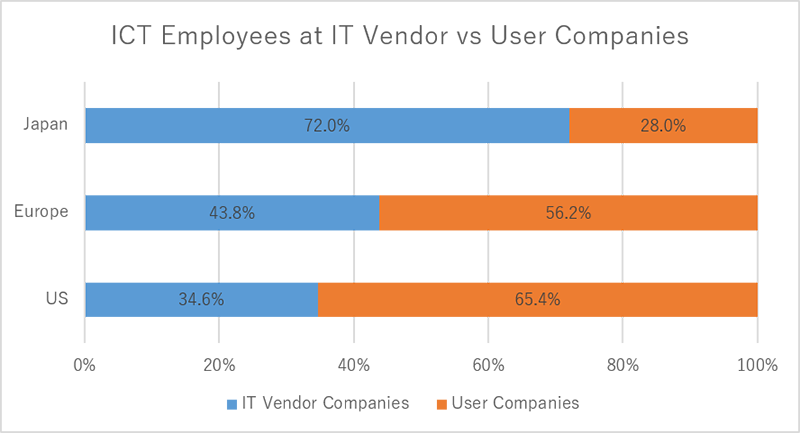
Figure 5: ICT employees at Vendor vs User companies
Data Source: [4] IPA, Japan White Paper on IT Human 2017
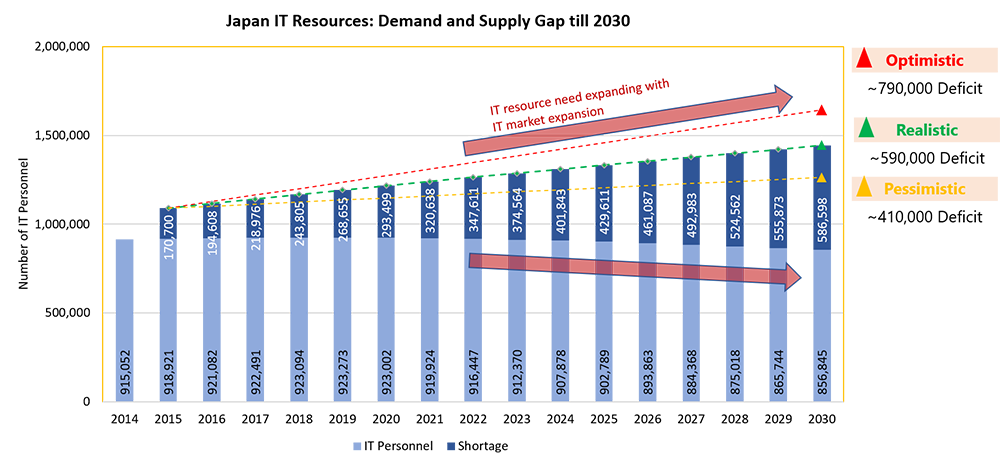
Figure 6: [3] Japan IT resources Demand -Supply gap
Note: Simulation is based on IT Market growth, productivity improvements of existing IT resources, automation
Data Source: Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry "Survey Results on the Latest Trends and Future Estimates of IT Human Resources" (commissioned by Mizuho Information & Research Institute)
Source: https://www.mizuho-rt.co.jp/publication/contribution/2018/zoom/mizuho-global1806-07_01.html
In Japan recently crisis concerning the shortage of IT skilled human resources is growing and visible. According to the report by The Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry's (METI) survey on the latest trends and future estimates of IT human resources, the shortage of IT personnel in Japan is likely to expand gradually from about 170,000 in 2015 to about 790,000 in 2030.
Considering 2019 data of IT human resources was about 923,000, the shortage by 2030 of 790,000 is quite significant. This unavailability of IT personnel is becoming an issue for IT related companies who provides specialised services as well as for companies that consume these services in their business. [3]
As IT is becoming part of our daily lives, the use of IT in all areas is growing rapidly. The digital transformation of businesses and innovations using cutting-edge technologies such as Cloud, AI, IoT is attracting increasing attention. Also forecasts around newer applications and usage of these technologies in all fields. However, the supply of "Skilled IT human resources" who can support this development has not scaled up to match the demand.
Few key reasons behind lack of supply of IT human resources in Japan are: [3]
- 1)Structural problem: In Japan, young people population is declining due to the declining year on year due to decline in birth-rate and increase in aging population. Each industry continues to compete for excellent new graduates in the new graduate recruitment market.
- 2)Economical boon vs shortage: Shortage situation is spurring mainly as the continuation of the "seller's market" in the booming economy. Expansion of IT needs and Japan specific structural issue widening this issue of skilled IT human resources.
- 3)Attractiveness vs capability: With global and domestic demand growing "attractiveness" of working as an IT human resource in a Japanese company is in mainstream. But the question is are the domestic excellent IT human members are enough active to play role at global level? Such capability problem can be behind the lack of "quality" in IT human resources.
2.4. Offshoring
Most of the IT offshoring of work (to different counties) is performed by US companies. North America has big pie with 46+% followed by Western Europe with 22% and 3rd Japan with 15%, less offshoring as compared to western counterparts.
Japanese companies face few challenges in offshoring, such as,
- 1.Language: though it is something which needs lot of energy, but that is the easier piece to deal with, as compared to other challenges.
- 2.Culture: every country has their own culture aspects, but Japan being a homogeneous country and a closed society, the culture is quite unique and challenging for foreigners to understand and adapt
- 3.Quality over Quantity: quality expectations, especially when we are in services business, the expectations of quality are quite high and in a high context environment here, it makes it even more challenging.
For Japanese companies China was the major offshoring destinations till 2010. Now in recent decade the offshoring focus shifted from China to Vietnam. Vietnam tops with more than 50% stake.

Figure 7: Japan Offshoring Challenges
India with greater than 2.1 million IT engineers is the third highest in the world. India becoming next favorable destination for Japanese companies to offshore work. Mainly due to ample availability of IT skilled human resources, favorable conditions, and adoption of cutting-edge digital technologies by IT people, innovation culture with technology startups and India being one of the major countries incubating the technology startups and ecosystem. Offshoring to India shares few major advantages for Japanese companies like their focus on processes and quality, Digital technology capabilities, faster adoption, innovative culture, gaining experience in Japanese bilingual coordination, greater flexibility, and global customer delivery experience.
3. Summary
In this column we tried to explain about Japanese IT services market, business structure, challenges for offshoring or global sourcing. Customers are actively trying to find outsourcing opportunities. Global sourcing and global business expansion should be the centre of the strategies for offshoring.
NTT DATA INTELLILINK Corporation has global delivery capabilities with offshore centre and wide experience to serve domestic and global customers.
In subsequent columns, we will focus on how India as offshoring and global sourcing destination for Japanese Prime Vendors and User Companies, Cultural differences, processes, tools, governance, and how successful global delivery can be accomplished etc.
References:
- [1]Global IT services:
https://www.statista.com/outlook/tmo/it-services/worldwide - [2] Japan IT Services:
https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prJPJ48879822
https://www.publickey1.jp/blog/22/2021it590003212ntt3idc_japan.html - [3]Japan IT Demand-Supply
https://www.mizuho-rt.co.jp/publication/contribution/2018/zoom/mizuho-global1806-07_01.html - [4]Resources: IPA 2017 IT Personnel white paper
https://www.ipa.go.jp/files/000059086.pdf - [5]Offshoring:
https://www.offshore-kaihatsu.com/how-to/ - [6]JETRO ICT report
https://www.jetro.go.jp/ext_images/en/invest/img/attractive_sectors/ict/ict_EN_202103.pdf - [7]System Integrators in Japan
https://ubv.vc/contents/trends/system-integrators/ - [8]IT services
https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/it-services - [9]Global IT engineers report:
https://git.resocia.jp/info/post-developers-around-the-globe-survey/
- Note:All logos are protected by respective laws. They are reproduced here for introductory and educational purposes only.